Product Details;
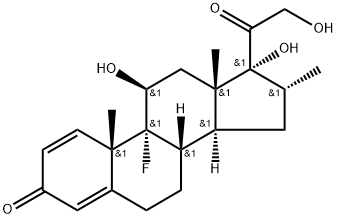
CasNo: 50-02-2
Molecular Formula: C22H29FO5
Appearance: White crystalline solid
|
50-02-2 Name |
|
|
Name |
DXM |
|
Synonym |
Dexamethasone;DEXAMETHASONE BASE;DEXAMETHASONUM;DEXAMETHASON;DEXAMETHASONE;CALONAT;(11BETA,16ALPHA)-9-FLUORO-11,17,21-TRIHYDROXY-16-METHYLPREGNA-1,4-DIENE-3,20-DIONE;(11B,16A)-9-FLUORO-11,17,21-TRIHYDROXY-16-METHYL-PREGNA-1,4-DIENE-3,20-DIONE;1,4-PREGNADIEN-9ALPHA-FLUORO-16ALPHA-METHYL-11BETA, 17ALPHA, 21-TRIOL 3,20-DIONE |
|
50-02-2 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid receptor agonist. |
|
Related Catalog |
Signaling Pathways >> Autophagy >> Autophagy Signaling Pathways >> GPCR/G Protein >> Glucocorticoid Receptor Signaling Pathways >> Autophagy >> Mitophagy Research Areas >> Inflammation/Immunology |
|
Target |
Glucocorticoid receptor[1] |
|
In Vitro |
Dexamethasone regulates several transcription factors, including activator protein-1, nuclear factor-AT, and nuclear factor-kB, leading to the activation and repression of key genes involved in the inflammatory response[1]. Dexamethasone potently inhibits granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) release from A549 cells with EC50 of 2.2 nM. Dexamethasone (EC50=36 nM) induces transcription of the β2-receptor is found to correlate with glucocorticoid receptor (GR) DNA binding and occurred at 10-100 fold higher concentrations than the inhibition of GM-CSF release. Dexamethasone (IC50=0.5 nM) inhibits a 3×κB (NF-κB, IκBα, and I-κBβ), which is associated with inhibition of GM-CSF release[2]. |
|
In Vivo |
It has previously been reported that treatment with Dexamethasone at a dose of 2×5 mg/kg efficiently inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation. In our experimental system, treatment with a single dose of Dexamethasone 10 mg/kg (i.p.) significantly decreases recruitment of granulocytes as well as spontaneous production of oxygen radicals compared with animals expose to LPS and injected with solvent alone (saline). The effects are statistically significant when administered both 1 h before and 1 h after inhalation of LPS. The number of granulocytes in BALF decreased to levels comparable to healthy animals (given an aerosol of water)[3]. Rats treated with Dexamethasone consume less food and weighed less than control rats. Treated rats also weigh less than pair-fed animals though their food intake is similar. Five days of Dexamethasone injection result in a significant increase in both the liver mass (+42%) and the liver to body weight ratio (+65%). The wet weight of gastrocnemius muscle decreases 20% after 5 days of treatment, but it remains unaffected relative to body weight (g/100 g body weight), indicating that muscle weight loss paralleled body weight loss[4]. |
|
References |
[1]. LaLone CA, et al. Effects of a glucocorticoid receptor agonist, Dexamethasone, on fathead minnow reproduction, growth, and development. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2012 Mar;31(3):611-22. [2]. Adcock IM, et al. Ligand-induced differentiation of glucocorticoid receptor (GR) trans-repression and transactivation: preferential targetting of NF-kappaB and lack of I-kappaB involvement. Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Jun;127(4):1003-11 [3]. Rocksén D, et al. Differential anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative effects of Dexamethasone and N-acetylcysteine in endotoxin-induced lung inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol. 2000 Nov;122(2):249-56 [4]. Roussel D, et al. Dexamethasone treatment specifically increases the basal proton conductance of rat liver mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 2003 Apr 24;541(1-3):75-9. [5]. Maher HM, et al. Simultaneous determination of selected tyrosine kinase inhibitors with corticosteroids and antiemetics in rat plasma by solid phase extraction and ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: Application to pharmacokinetic interaction studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 May 30;124:216-27. |
|
50-02-2 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
255-264ºC |
|
Boiling point |
568.2±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C22H29FO5 |
|
Molecular Weight |
392.461 |
|
Flash Point |
297.5±30.1 °C |
|
PSA |
94.83000 |
|
LogP |
1.87 |
|
Exact Mass |
392.199890 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±3.5 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.592 |
|
50-02-2 Description |
|
Dexamethasone is an Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid that is used to treat inflammatory and autoimmune conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and bronchospasm. It is useful to study apoptosis, cell signaling pathways and gene expression. It is associated with marbofloxacin and clotrimazole and finds application in veterinary medicine to treat difficult ear infections in dogs. It is also used to treat horses with swelling of of distal limbs and general bruising in combination with trichlormethiazide. |
|
50-02-2 Uses |
|
Dexamethasone is used for the same indications as all corticosteroids; however, it exhibits a significantly more powerful anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic action. It is used for circulatory collapse—shock during or after surgical operations, trauma, blood loss, myocardial infarction, and burns. It is also used in severe infections—toxemia, vascular collapse in meningococcosis, septicemia, diphtheria, typhoid fever, and peritonitis. It is used in severe allergic conditions—asthmatic status, laryngeal edema, severe anaphylactic reactions to medicinal drugs, and pyrogenic reactions. |
Relevant Products
-
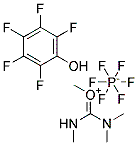
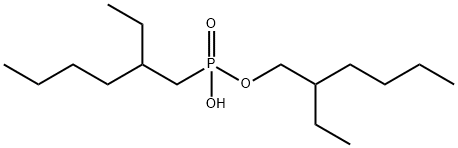
2-ethylhexyl hydrogen -2-ethylhexylphosphonate
CAS:14802-03-0
-
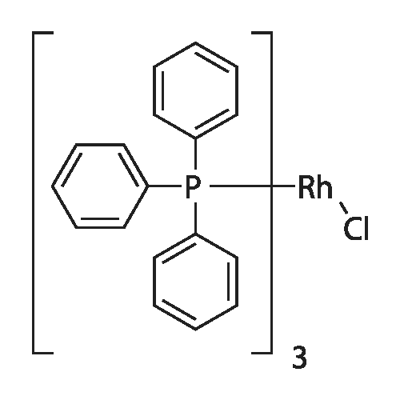
Chlorotris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I)
CAS:14694-95-2