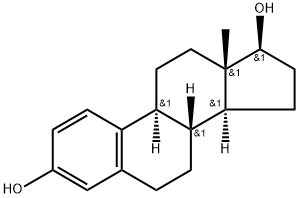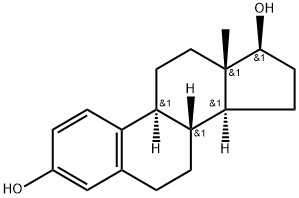
Product Details;
CasNo: 50-28-2
Molecular Formula: C18H24O2
Appearance: white crystalline powder
|
50-28-2 Name |
|
|
Name |
Estradiol |
|
Synonym |
BETA-ESTRADIOL-16,16,17-D3;17BETA-ESTRADIOL-16,16,17-D3;β-Estradiol, 99% (dry wt.), ca 3% water;1,3,5-Estratriene-3,17beta-diol;17beta-Estradiol;3,17beta-Dihydroxy-1,3,5(10)-estratriene;Dihydrofolliculin;Estradiol |
|
50-28-2 Biological Activity |
|
|
Description |
Estradiol is a steroid sex hormone vital to the maintenance of fertility and secondary sexual characteristics in females. |
|
Related Catalog |
Signaling Pathways >> Others >> Estrogen Receptor/ERR Research Areas >> Endocrinology Natural Products >> Steroids |
|
Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
|
In Vitro |
Estradiol causes new dendritic spines and synapses in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. Estradiol increases NMDA receptor binding by 46% in parallel with dendritic spine and synapse density. Estradiol also elevates sensitivity of CA1 pyramidal cells to NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic input and such an effect is correlated with the estradiol-induced increase in dendritic spine density in the apical dendritic tree of these cells[1]. Estradiol reduces Ba2+ entry reversibly via Ca2+ channels in acutely dissociated and cultured neostriatal neurons. Estradiol also reduces Ba2+ currents but is significantly less effective than Estradiol in rat neostriatal neurons[2]. Estradiol dose-dependently inhibits IL-1-, TNF-, and IL-1 and TNF-induced production of bioassayable IL-6. Estradiol blocks TNF-induced IL-6 production and osteoclast development in primary bone cell cultures derived from neonatal murine calvaria. |
|
In Vivo |
Estradiol functions in hippocampal synapse density during the estrous cycle in the adult rat[4]. Estradiol reverses the ovariectomy-induced decrease in spine density. Estradiol in combination with progesterone enhances spine density for 2 to 6 h but decreases following estradiol alone. |
|
Cell Assay |
Briefly, B9 cells (5×103/well of a 96-well plate) are cultured with a series of dilutions of the supernatants in a final volume of 100 mL of RPMI 1640, supplemented with 5×10-5mol/Lof 2-mercaptoethanol, 10% FBS, 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin in flat-bottom microtiter plates. After 42 h, 0.5 μCi of [3H]thymidine is added. 6 h later, the cells are harvested and the radioactivity incorporated is determined. IL-6 is quantitated from a standard curve set up with known amounts of recombinant human or mouse IL-6. The anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibody completely inhibited the ability of the B9 cells to proliferate in response to recombinant mouse IL-6. In addition, we determined that B9 cells do not proliferate in response to IL-I or TNF, and that antibodies to these two cytokines did not affect the cell proliferation in response to IL-6. Further, it is established that neither Estradiol (17β-estradiol), nor the 0.01% ethanol used as vehicle in these experiments, has any effect on the bioassay. |
|
Animal Admin |
Adult female Sprague Dawley rats are housed on a 12 hr light/dark cycle with unlimited access to food and water. These animals are left gonadally intact (intact), ovariectomized and treated with estradiol benzoate (OVX+E), or ovariectomized and treated with sesame oil vehicle (OVX+O). The hormone treatment regimen that is used in these experiments has been shown previously to result in differences in CA1 pyramidal cell dendritic spine and synapse density. Six days before electrophysiological analysis, animals are ovariectomized under Metofane anesthesia using aseptic surgical procedure. After surgery, animals are housed individually. On days 3 and 4 after surgery, OVX+E animals are injected (s.c.) with 10 μg of 17β-estradiol benzoate in 100 μL of sesame oil vehicle; OVX+O animalsreceive oil vehicle at each injection time. Forty-eight hours after the second estradiol or vehicle injection, animals are killed by decapitation and hippocampal slices are prepared from their brains. Gonadally intact animals are killed at random stages of the estrous cycle. |
|
References |
[1]. Woolley CS, et al. Estradiol increases the sensitivity of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells to NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic input: correlation with dendritic spine density. J Neurosci. 1997 Mar 1;17(5):1848-59. [2]. Mermelstein PG, et al. Estradiol reduces calcium currents in rat neostriatal neurons via a membrane receptor. J Neurosci. 1996 Jan 15;16(2):595-604. [3]. Girasole G, et al. 17 beta-estradiol inhibits interleukin-6 production by bone marrow-derived stromal cells and osteoblasts in vitro: a potential mechanism for the antiosteoporotic effect of estrogens. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):883-91. [4]. Woolley CS, et al. Estradiol mediates fluctuation in hippocampal synapse density during the estrous cycle in the adult rat. J Neurosci. 1992 Jul;12(7):2549-54. [5]. Woolley CS, et al. Roles of estradiol and progesterone in regulation of hippocampal dendritic spine density during the estrous cycle in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Oct 8;336(2):293-306. |
|
50-28-2 Chemical & Physical Properties |
|
|
Melting point |
173ºC |
|
Boiling point |
445.9±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
|
Density |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|
Molecular Formula |
C18H24O2 |
|
Molecular Weight |
272.382 |
|
Flash Point |
209.6±23.3 °C |
|
PSA |
40.46000 |
|
LogP |
4.13 |
|
Exact Mass |
272.177643 |
|
Vapour Pressure |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
|
Index of Refraction |
1.599 |
|
Storage condition |
2-8°C |
|
Stability |
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
|
solubility |
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in acetone, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
|
storage temp. |
room temp |
|
50-28-2 Description |
|
β-Estradiol is an endogenous estrogenic hormone receptor (ER) agonist (Ki values are 0.12 and 0.13 nM for ERα and ERβ respectively). Also high affinity ligand at membrane estrogen GPR30 receptors. β-Estradiol is an activator of PI 3-kinase. Estradiol (17β-estradiol, β-Estradiol, E2, 17β-Oestradiol) is a human sex hormone and steroid, and the primary female sex hormone. Estradiol upregulates IL-6 expression through the estrogen receptor β (ERβ) pathway. |
|
50-28-2 Uses |
|
|
50-28-2 Safety Profile |
|
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic, neoplastigenic, tumorigenic, and teratogenic data. A promoter. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: ferthty effects. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. A steroid hormone much used in medicine. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes. |
|
50-28-2 Purification Methods |
|
17-Estradiol (previously known as -estradiol) is purified by chromatography on SiO2 (toluene/EtOAc 4:1) and recrystallised from CHCl3/hexane or 80% EtOH. It is stable in air, is insoluble in H2O, and is precipitated by digitonin. The UV has max at 225 and 280 nm. The diacetate [3434-88-6] has m 97-98o and forms leaflets from aqueous EtOH. The 3-benzoate crystallises from aqueous MeOH withm 193o and [] D 25 +58o to 63o (c 1, dioxane). [Meischer & Scholz Helv Chim Acta 20 263, 1237 1937, Biochem J 32 1273 1938, Oppolzer & Roberts Helv Chim Acta 63 1703 1980, Inhoffen & Zühlsdorff Chem Ber 7 4 1914 1941, Beilstein 6 IV 6611.] |
Relevant Products
-
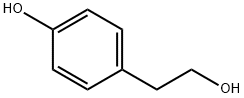
4-Hydroxyphenethyl alcoholCAS NO.: 501-94-0
CAS:501-94-0
-
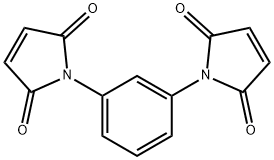
N,N'-1,3-Phenylene bismaleimide
CAS:3006-93-7
-
Estradiol
CAS:50-28-2